Drop Forging Services
On this page
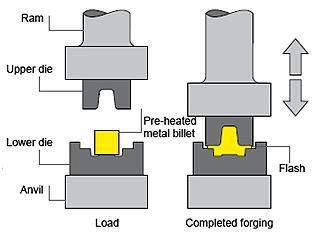
Drop forging is a metal shaping technique where an ingot or metal workpiece is subjected to compression by a hammer, resulting in its transformation and conformity to the shape of a die or set of dies. Drop forging is widely utilized as the most common method of metal forging and can be applied in hot forging, warm forging, and cold forging, as well as both open die forging and closed die forging processes. This modernized form of smith forging replaces the manual force exerted by a blacksmith with a mechanized hammer made of hardened alloy steel, equipped with a specially designed die. By deforming the internal grain of the metal to match the shape of the desired part, forging enhances the strength and suitability of the metal for its specific application.
● Increased Production Efficiency
Drop forging results in higher production efficiency as the metal undergoes deformation within the mold cavity, allowing for the rapid attainment of the desired shape.
● Ability to Forge Complex-Shaped Metal Parts
The drop forging process enables the forging of intricate metal parts, and it ensures a more reasonable distribution of metal flow lines. Additionally, drop forging can enhance the lifespan of the forged parts.
● Accurate Size, Improved Surface Quality, and Reduced Machining Allowance
Drop forgings exhibit precise sizing, improved surface quality, and require smaller machining allowances. This leads to cost savings and better overall part quality.
● Material Savings and Reduced Machining
Drop forging minimizes material waste and reduces the need for extensive machining. In larger production batches, this process can effectively reduce the cost of spare parts.
● Easy Production Operation and Low Labor Requirement
Drop forging simplifies the production operation, resulting in lower labor requirements. This contributes to reduced workforce needs during the manufacturing process.
● High Initial Costs
Drop forging requires specialized equipment, such as hammers and dies, which can be expensive to set up initially. This may pose a barrier for small-scale or custom manufacturing operations.
● Limited Flexibility in Design Changes
Once the dies are created for drop forging, making design changes can be challenging and costly. Altering the shape or dimensions of the forged part often necessitates the creation of new dies, resulting in additional expenses and time.
● Material Limitations
Drop forging is most suitable for metals with good forgeability, such as steel, aluminum, brass, and titanium. However, it may not be feasible for materials with poor forgeability or those that require more intricate shaping.
● Size Limitations
The size of the forged parts is limited by the capacity of the forging equipment. Very large or oversized components may be challenging to produce using drop forging techniques.
● Drop forging presents a dangerous working environment
Drop forging is extensively used in the automotive industry for the production of components such as crankshafts, connecting rods, gears, axle beams, steering knuckles, and suspension parts. These critical components require high strength, durability, and dimensional accuracy, making drop forging an ideal manufacturing method.
● Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry relies on drop forging for producing components that demand exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to extreme conditions. Examples include landing gear components, engine shafts, structural parts, and wing attachments.
● Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas sector utilizes drop forging for producing valves, connectors, pipe fittings, drilling rig components, and other critical equipment that can withstand the demanding environments and pressures encountered in oil and gas exploration and production.
● Mining and Heavy Machinery
Drop forging is widely employed in the manufacturing of mining equipment, including drills, crusher parts, loader components, and gears. These forged parts need to endure rigorous conditions and heavy usage.
● Medical Equipment
Drop forging is utilized in the production of surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and other medical equipment that require high strength, precision, and biocompatibility.
Ultimately, the selection of the process hinges on the specific product requirements and the type of metal to be employed. All forging methods have the potential to serve as effective means for reinforcing and shaping your metal workpieces into the desired end product.
● Increased Production Efficiency
Drop forging results in higher production efficiency as the metal undergoes deformation within the mold cavity, allowing for the rapid attainment of the desired shape.
● Ability to Forge Complex-Shaped Metal Parts
The drop forging process enables the forging of intricate metal parts, and it ensures a more reasonable distribution of metal flow lines. Additionally, drop forging can enhance the lifespan of the forged parts.
● Accurate Size, Improved Surface Quality, and Reduced Machining Allowance
Drop forgings exhibit precise sizing, improved surface quality, and require smaller machining allowances. This leads to cost savings and better overall part quality.
● Material Savings and Reduced Machining
Drop forging minimizes material waste and reduces the need for extensive machining. In larger production batches, this process can effectively reduce the cost of spare parts.
● Easy Production Operation and Low Labor Requirement
Drop forging simplifies the production operation, resulting in lower labor requirements. This contributes to reduced workforce needs during the manufacturing process.
● High Initial Costs
Drop forging requires specialized equipment, such as hammers and dies, which can be expensive to set up initially. This may pose a barrier for small-scale or custom manufacturing operations.
● Limited Flexibility in Design Changes
Once the dies are created for drop forging, making design changes can be challenging and costly. Altering the shape or dimensions of the forged part often necessitates the creation of new dies, resulting in additional expenses and time.
● Material Limitations
Drop forging is most suitable for metals with good forgeability, such as steel, aluminum, brass, and titanium. However, it may not be feasible for materials with poor forgeability or those that require more intricate shaping.
● Size Limitations
The size of the forged parts is limited by the capacity of the forging equipment. Very large or oversized components may be challenging to produce using drop forging techniques.
● Drop forging presents a dangerous working environment
- Equipment Failure: The heavy impact and force involved in drop forging can put significant stress on the forging equipment, such as hammers or presses. There is a risk of equipment failure or breakdown, which can lead to production delays and increased costs.
- Safety Hazards: Working with heavy machinery and high temperatures involved in drop forging presents inherent safety hazards. Proper safety measures, including protective gear and training, must be implemented to minimize the risk of accidents or injuries to operators.
- Heat-Related Issues: In hot or warm forging processes, the high temperatures involved can pose risks such as burns or fire hazards. Adequate temperature control measures, cooling systems, and proper handling procedures must be followed to mitigate these risks.
Drop forging is extensively used in the automotive industry for the production of components such as crankshafts, connecting rods, gears, axle beams, steering knuckles, and suspension parts. These critical components require high strength, durability, and dimensional accuracy, making drop forging an ideal manufacturing method.
● Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry relies on drop forging for producing components that demand exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to extreme conditions. Examples include landing gear components, engine shafts, structural parts, and wing attachments.
● Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas sector utilizes drop forging for producing valves, connectors, pipe fittings, drilling rig components, and other critical equipment that can withstand the demanding environments and pressures encountered in oil and gas exploration and production.
● Mining and Heavy Machinery
Drop forging is widely employed in the manufacturing of mining equipment, including drills, crusher parts, loader components, and gears. These forged parts need to endure rigorous conditions and heavy usage.
● Medical Equipment
Drop forging is utilized in the production of surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and other medical equipment that require high strength, precision, and biocompatibility.
Ultimately, the selection of the process hinges on the specific product requirements and the type of metal to be employed. All forging methods have the potential to serve as effective means for reinforcing and shaping your metal workpieces into the desired end product.
Next: Open Die Forging Services
Previous: Hot Forging Services

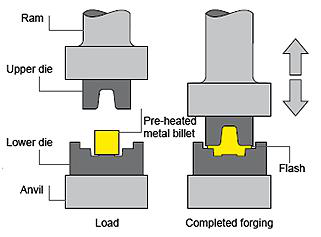 What Is Drop Forging?
What Is Drop Forging?