Automobile & Vehicle

On this page
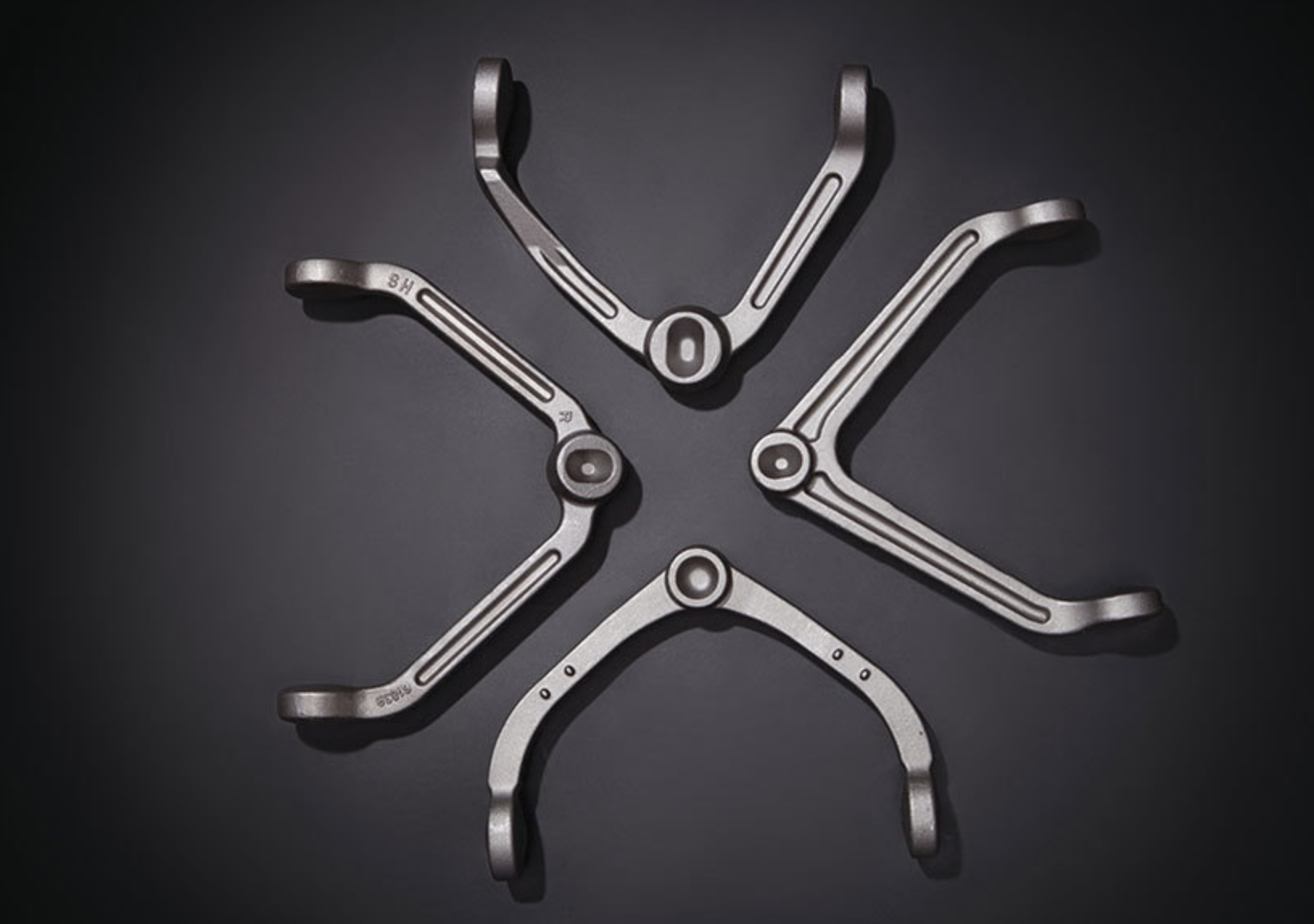
Forged parts are crucial in the automotive industry, offering exceptional strength, durability, and precision. They play vital roles in engine components, transmissions, chassis, and more, ensuring reliability and longevity. Despite potential higher upfront costs, their long-term benefits include reduced maintenance and replacement needs, making them a cost-effective choice in automobile manufacturing.
Forged components enjoy extensive use in the automotive sector because of their exceptional strength, durability, and precision. Below are several prevalent types of forged parts employed in automobiles:
●Crankshafts
●Connecting rods
●Gears
●Axles
●Control arms
●Steering Components
●Wheel Hubs
●Spindles
●Camshafts
●Tie-Rod Ends
●Transmission Shafts
●Axle components
●Joints
●Bearings
Forged automotive components offer numerous significant benefits, playing a crucial role in their extensive adoption within the automotive sector:
1. Weight Reduction: Forging enables the fine-tuning of the weight-to-strength ratio of components, a critical consideration in automotive engineering. This optimization is especially pertinent in vehicle design, where weight reduction can enhance fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
2. Durability and Longevity: Forged parts enjoy exceptional strength, which leads to outstanding durability and an extended operational lifespan, thereby reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance requirements.
3. Improved Fatigue Resistance: Forged components demonstrate outstanding resistance to fatigue, rendering them suitable for parts exposed to cyclic loading, such as crankshafts and connecting rods. They can endure millions of cycles without succumbing to fatigue failures.
4. Cost-effectiveness: Although forged automotive components may entail a higher initial investment compared to cast or machined parts, their extended lifespan and reduced replacement frequency often result in long-term cost-effectiveness.
2. Durability and Longevity: Forged parts enjoy exceptional strength, which leads to outstanding durability and an extended operational lifespan, thereby reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance requirements.
3. Improved Fatigue Resistance: Forged components demonstrate outstanding resistance to fatigue, rendering them suitable for parts exposed to cyclic loading, such as crankshafts and connecting rods. They can endure millions of cycles without succumbing to fatigue failures.
4. Cost-effectiveness: Although forged automotive components may entail a higher initial investment compared to cast or machined parts, their extended lifespan and reduced replacement frequency often result in long-term cost-effectiveness.
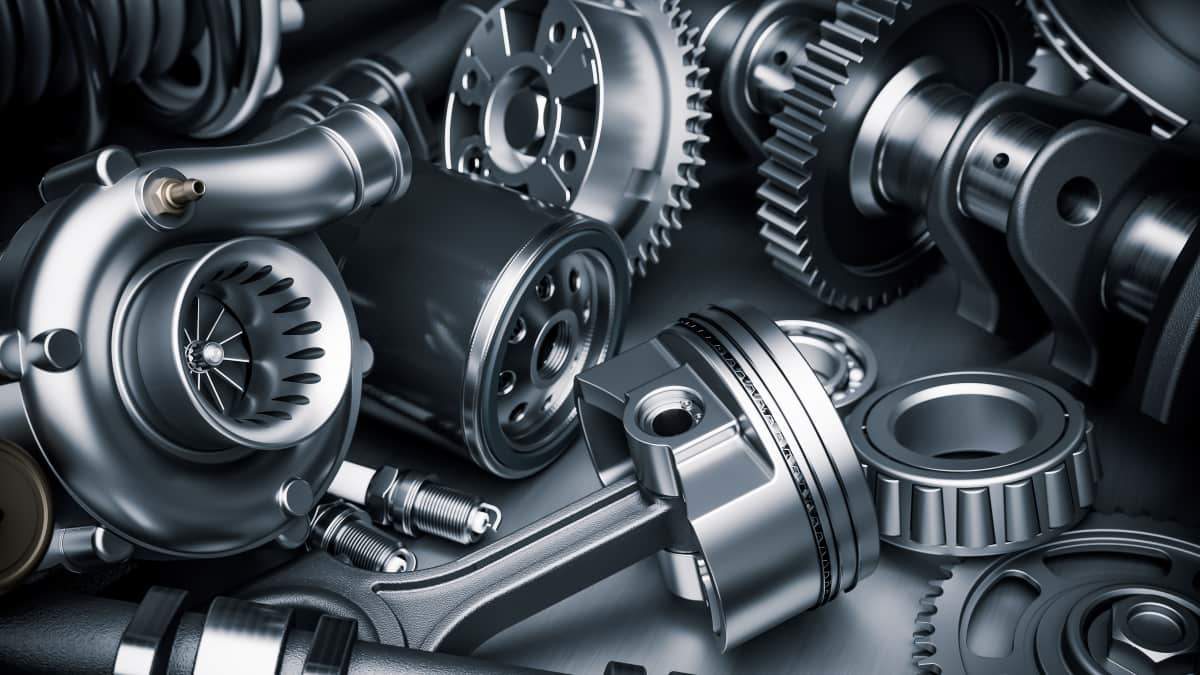
 Applications in Automobile Manufacturing
Applications in Automobile Manufacturing